What is Decentralization?
Decentralization
Decentralization is the distribution of decision-making power and authority in a business or organization instead of having one person make all decisions. This is usually done to help the company grow and increase efficiency. It’s also used to protect from any one employee getting too powerful and controlling the entire company.
In a political context, Decentralization refers to the transfer of specific types of decision-making and administrative authority from national or higher-level entities to subordinate field, regional, and local governments. It may also include transfers of authority and responsibility for public functions to private sector organizations.
It can likewise refer to the dispersion of assets so that guaranteed services are furnished with better execution and consistency, just as a decreased probability of explosive letdown. A notable example of this is the blockchain, a distributed database that stores a library of resources and trades across a peer-to-peer network. This is not just limited to financial data, however, and can additionally incorporate information regarding ownership, agreements, products, and some other aspects of a network’s ecosystem.
What is Decentralization?
A decentralized network is a type of computer networking whereby each machine on the network acts as its own server rather than being connected to a central server. This means that if one server goes down, the entire network can continue to operate. Additionally, because of this structure the security of a decentralized network is much more robust as hackers are not able to target the central server.
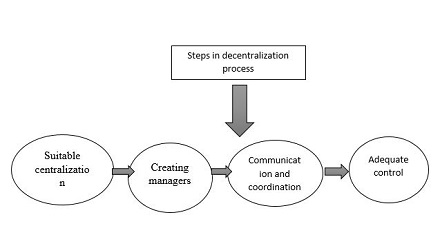
There are many different kinds of decentralization, and each should be analyzed with respect to its particular political, economic and social environment before determining if it is the right solution. For example, in a democratic system of government, decision-making and administrative authority might be transferred to regional and local governments while maintaining authority to establish broad policy guidelines. Similarly, private corporations might be given autonomy to manage specific business activities and markets while the overall direction of the firm is still maintained by top management.
In a business setting, decentralization can be beneficial for companies with remote employees or those that operate in multiple locations. In these situations, it allows upper-level management to focus on growth opportunities and major decisions while allowing middle- and lower-level managers the freedom to execute day-to-day tasks. In the long run, this can result in more efficient operations and improved productivity.
On the downside, a decentralized organizational structure can lead to confusion. When each department has its own team leaders with their own opinions and schedules, it can be difficult to communicate consistently. It’s important to find the best leadership model for your company’s needs and goals. If you need help boosting your team’s leadership skills, our BetterUp program is here to help. Request a demo today to learn more.